1. Questions
The COVID-19 pandemic caused many countries to implement social distancing measures that prevented people from attending their workplaces. While some individuals were able to transfer their work activities to their residences, others had work hours reduced or even lost their jobs. By investigating the observed variation in the location and the time allocated to work during the pandemic by different segments of the workforce, the current study adds to the growing body of literature on COVID-19 effects on work activities (for example, Astroza et al. 2020; Beck and Hensher 2022) and complements previous work that classified occupations and socio-demographic characteristics associated with the feasibility of working from home (WFH) (Dingel and Neiman 2020; Mongey, Pilossoph, and Weinberg 2020). In specific, we identify what types of individuals (1) decreased/increased the total hours worked, (2) substituted out-of-home work (OHW) by WFH, (3) whether individuals’ productivity was affected, and (4) how these changes varied between American states with mild- and high-incidence of COVID-19.
2. Methods
Firstly, we extracted individual socio-demographic characteristics, work location, and time use information from the American Time Use Survey (ATUS) in a pre-pandemic (2019) and pandemic (2020) context (US-BLS 2021). The final sample included 7636 individuals in the workforce and is described in Appendix A and B. Since the data from both years are not panel, we conducted chi-squared tests across all socio-demographic variables to evaluate whether the samples from 2019 and 2020 were comparable. We concluded that the comparison was valid as the only statistically significant differences observed were the widespread increase in unemployment, and an increase in the number of high-income individuals living in metropolitan areas in 2020, which both are likely associated with the pandemic.
Secondly, we matched the ATUS observations with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDCP 2021) data, which showed the temporal distribution of COVID-19 cases throughout 2020. The daily number of confirmed cases at the state level 7, 14, 21, and 28 days prior to the ATUS diary recording date was used to compute COVID-19 incidence by population size. Three categories of incidence severity were established: (1) no-COVID-19 (2019 observations and 2020 observations in places with zero cases); (2) mild incidence (incidence ≤ 90th percentile of all individuals in the non-zero incidence places) and (3) high incidence (incidence > 90th percentile).
Thirdly, a latent class multiple discrete-continuous model was estimated to identify subclasses of individuals in the workforce with differences in the time allocated to work at three locations: (1) workplace, (2) home, and (3) other places. The time allocated to non-work activities was considered the base category to enable the identification of overall increases and reductions in time dedicated to work activities. Readers can refer to Bhat et al. (2008) and Hess and Palma (2019) for the methodology of the latent-class MDCEV model with outside goods used in this study. We used the R package Apollo (version 0.2.5) for the estimation (Hess and Palma 2021).
Finally, to facilitate the interpretation of our model results, we calculated the odds ratio (OR) associated with the class membership variables and the average treatment effects (ATE) of COVID-19 incidence on each class stratified by socio-demographic groups (Sarrias and Daziano 2018; Etzioni et al. 2021). Average fitted values for socio-demographic groups under each class were calculated considering that all individuals were in no (control), mild (treatment 1), and high (treatment 2) COVID-19 incidence situations. ATE are then extracted from the relative comparison between the fitted values in control and treatment situations. Since ATE are aggregate statistics and the probability of belonging to a class varies across individuals, instead of using an arithmetic average of the observations in each group, we computed a weighted-average based on the class-probability to obtain the final treatment effects, as described in detail in Appendix C.
3. Findings
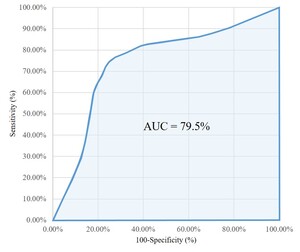
The bottom half of Table 1 shows that two latent classes of workers were identified in the final model specification, with Class 1 being twice the size of Class 2. To evaluate the quality of the classification, a receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve was fitted and the area under the curve (AUC) measured, as illustrated in Figure 1 (see Hosmer and Lemeshow 2020, for method details). The AUC suggests the latent class classification has a 79.5% chance of accurately distinguishing an individual between two classes. As a rule of thumb, an 80% classification performance is considered excellent (Hosmer and Lemeshow 2020).

Figure 1.ROC curve and AUC.
Sensitivity (%) = the number of correctly identified individuals in class 2/total number of individuals in class 2
Specificity (%) = the number of correctly identified individuals in class 1/total number of individuals in class 1.
Young males with lower levels of education and low to medium income are more likely to belong to Class 1. In contrast, middle-aged women with tertiary education and high-income are more likely to belong to Class 2. The contribution of each one of the socio-demographic characteristics to the likelihood of belonging to one of these classes is demonstrated in the OR column. The strongest distinction between the two classes is regarding the level of education, as individuals who have higher education degrees are four times more likely to belong to Class 2 than those who do not have degrees.
The top half of Table 1 shows the estimated MDCEV coefficients, while Table 2 shows the average treatment effects calculated based on these coefficients. We observe that individuals in Class 1 decreased their total work time during the pandemic, with service/manual labor, healthcare, and legal employees in both low-mid and high incidence places showing the greatest reduction.
Table 1.Results of the outside-good latent-class multiple discrete-continuous extreme value model (LC-MDCEV).
| Variable |
Workplace |
Home |
Other places |
| Class 1 |
Class 2 |
Class 1 |
Class 2 |
Class 1 |
Class 2 |
| Coef./s.e. (t-stat) |
Coef./s.e. (t-stat) |
Coef./s.e. (t-stat) |
Coef./s.e. (t-stat) |
Coef./s.e. (t-stat) |
Coef./s.e. (t-stat) |
| Constant |
-12.34/0.70 (-17.40) |
-11.98/0.51 (-23.44) |
-8.11/0.16 (-49.55) |
-10.29/0.33 (-31.01) |
-10.48/0.37 (-28.05) |
| Managers, professionals, education- and art-related employees (base: unemployment) |
4.89/0.71 (6.87) |
3.54/0.73 (4.82) |
1.57/0.46 (3.41) |
0.42/0.13 (3.38) |
|
0.75/0.32 (2.33) |
| Service/manual labor, healthcare, and legal-related employees (base: unemployment) |
5.23/0.71 (7.37) |
4.40/0.72 (6.12) |
|
|
0.66/0.33 (2.00) |
1.19/0.39 (3.08) |
| Self-employed workers (base: unemployment) |
4.80/0.72 (6.70) |
3.05/0.87 (3.52) |
3.18/0.49 (6.55) |
1.16/0.18 (6.35) |
1.51/0.33 (4.60) |
|
| Metropolitan residents (base: non- metropolitan) |
|
|
|
0.37/0.12 (3.23) |
-0.29/0.13 (-2.24) |
|
| Mild incidence [7 days] (base: no-COVID-19) |
-0.24/0.06 (-3.81) |
-0.96/0.19 (-4.94) |
|
0.70/0.13 (5.50) |
|
-0.40/0.11 (-3.71) |
| High incidence [7 days] (base: no-COVID-19) |
|
-0.26/0.11 (-2.31) |
|
0.97/0.17 (5.84) |
|
|
| Mild incidence [7 days] x Managers, professionals, educational and art-related employees |
|
|
|
0.55/0.17 (3.34) |
|
|
| Mild incidence [7 days] x Self-employed workers |
|
|
|
-0.44/0.20 (-2.18) |
|
|
| High incidence [7 days] x Metropolitan residents |
|
|
|
|
-0.86/0.37 (-2.36) |
|
| Latent class model component |
| Class membership variable |
Membership parameters
Coef./s.e. (t-stat) |
Odds ratio of belonging to Class 2 |
| Class 1 |
Class 2 |
| Constant |
Fixed |
-1.75/0.18 (-9.87) |
0.17 |
| Age >= 40 (base: Age 18-39) |
Fixed |
0.43/0.09 (4.59) |
1.54 |
| Male (base: female) |
Fixed |
-0.45/0.10 (-4.59) |
0.64 |
| Bachelor’s and higher degree (base: without a bachelor’s degree) |
Fixed |
1.40/0.11 (12.99) |
4.06 |
| High income (base: low, medium income) |
Fixed |
0.46/0.10 (4.65) |
1.58 |
| Summary of class allocation for the latent class model component (mean probability) |
66.65% |
33.35% |
- |
LL: -41987.44; LL Class 1: -44044.70; LL Class 2: -45299.67;
Alpha: Fixed to -1000 for all alternatives (γ-profile MDCEV); Gamma: (1) workplace= 414.90, (2) home= 86.56, and (3) other places=128.77
Table 2.Average treatment effects on time allocation (based on the probability-weighted fitted value).
| Variable |
Class 1 (n=5717) |
Class 2 (n=1919) |
| Non-work |
Workplace |
Home |
Other places |
Non-work |
Workplace |
Home |
Other places |
| CONTROL: Fitted values considering all individuals in the no COVID-19 incidence (average minutes per individual) |
| All individuals |
1170.69 |
249.83 |
6.50 |
12.98 |
1225.23 |
90.53 |
109.40 |
14.84 |
| Unemployed |
1427.32 |
2.33 |
2.12 |
8.23 |
1348.13 |
1.75 |
84.48 |
5.64 |
| Managers, professionals, education- and art-related employees |
1191.49 |
227.90 |
7.81 |
12.80 |
1245.40 |
65.13 |
117.95 |
11.52 |
| Service/manual labor, healthcare, and legal employees |
1134.09 |
293.31 |
1.49 |
11.11 |
1205.22 |
143.17 |
74.38 |
17.23 |
| Self-employed workers |
1173.60 |
203.46 |
35.41 |
27.53 |
1176.82 |
37.11 |
203.59 |
22.48 |
| Non-metropolitan residents |
1168.80 |
249.39 |
5.19 |
16.62 |
1229.79 |
99.43 |
89.23 |
21.55 |
| Metropolitan residents |
1171.55 |
249.25 |
6.86 |
12.34 |
1224.03 |
89.84 |
111.92 |
14.21 |
| TREATMENT EFFECT 1: Differences of fitted values between the COVID-19 mild-incidence and no incidence (average minutes per individual) |
| All individuals |
36.67 |
-41.20 |
8.33 |
-3.80 |
-56.16 |
-56.81 |
118.29 |
-5.32 |
| Unemployed |
0.67 |
-0.45 |
2.34 |
-2.56 |
-61.25 |
-1.24 |
64.66 |
-2.17 |
| Managers, professionals, education- and art-related employees |
24.59 |
-40.61 |
19.97 |
-3.95 |
-133.64 |
-44.19 |
182.85 |
-5.02 |
| Service/manual labor, healthcare, and legal employees |
45.94 |
-44.47 |
1.66 |
-3.13 |
20.20 |
-86.16 |
71.22 |
-5.26 |
| Self-employed workers |
31.16 |
-35.02 |
12.16 |
-8.30 |
-15.18 |
-22.98 |
45.82 |
-7.66 |
| Non-metropolitan residents |
30.78 |
-31.38 |
5.00 |
-4.40 |
-20.17 |
-60.65 |
88.00 |
-7.18 |
| Metropolitan residents |
36.90 |
-41.56 |
8.36 |
-3.70 |
-58.85 |
-56.47 |
120.44 |
-5.12 |
| TREATMENT EFFECT 2: Differences of fitted value between the COVID-19 high-incidence and no incidence (average minutes per individual) |
| All individuals |
40.19 |
-45.69 |
11.20 |
-5.70 |
-85.84 |
-26.90 |
120.86 |
-8.12 |
| Unemployed |
0.63 |
-0.50 |
3.76 |
-3.89 |
-94.63 |
-0.58 |
98.27 |
-3.06 |
| Managers, professionals, education- and art-related employees |
35.68 |
-43.07 |
13.59 |
-6.20 |
-100.98 |
-21.22 |
128.87 |
-6.67 |
| Service/manual labor, healthcare, and legal employees |
51.37 |
-49.42 |
2.66 |
-4.61 |
-48.21 |
-39.58 |
96.69 |
-8.90 |
| Self-employed workers |
2.69 |
-45.75 |
54.99 |
-11.93 |
-152.55 |
-13.91 |
179.10 |
-12.64 |
| Non-metropolitan residents |
27.61 |
-37.86 |
8.91 |
1.34 |
-73.70 |
-28.00 |
103.81 |
-2.11 |
| Metropolitan residents |
41.51 |
-45.75 |
11.14 |
-6.90 |
-87.15 |
-26.85 |
122.85 |
-8.85 |
All effects are significant at p<0.05
Both Class 1 and 2 present some level of substitution of OHW by WFH; however, the magnitude of the transference of work to the residence is significantly higher for Class 2. These results support Mongey, Pilossoph, and Weinberg (2020) finding that older and more educated individuals (Class 2 profile) have more autonomy in their jobs. Managers, professionals, education, and art-related employees and self-employed workers reveal a greater propensity to WFH than others (in both classes and for both COVID-19 incidence levels), which is likely associated with the nature of their work tasks (Elldér 2020).
In general, Class 2 presents an increase in hours worked, showing that the transference of work to the residential setting may have decreased their productivity. Productivity losses seem higher among individuals living in metropolitan areas compared to regional areas, indicating that non-city residents were less affected by the pandemic, as also observed by Chauhan et al. (2021).
For Class 1, reductions in time spent in the workplace were similar for both low and high COVID-19 incidence states (except for self-employed workers, who were more affected in high-incidence locations). For Class 2, on the other hand, there were greater reductions in time spent in the workplace for mild-low incidence places, which may be associated with stricter work-related social distancing measures. However, the proportional increase in hours worked at home is also greater in high-incidence areas, showing either a more significant productivity loss or an increase in workload, especially for self-employed individuals.
In conclusion, our findings suggest the need to consider a combination of assistance measures when formulating policies to support workers during pandemic situations that require social distancing. These measures should take into consideration occupation and socio-demographic characteristics and address both differences in lost work opportunity and productivity changes. For example, policies should consider that middle-aged professional women are more likely to have an increase in hours worked and a decrease in productivity than other groups, and thus, additional support to prevent this decrease in productivity may be required.
Appendices
Appendix A
Table A1.Sample distribution of the outcome variable and the COVID-19 incidence variable.
| Year |
Alternative |
Number of individuals (%) |
Mean duration in minutes (std. dev) |
| Only spent time in one alternative |
Spent time in multiple alternatives |
Including all individuals |
Including only individuals who spent more than zero minutes |
| 2019 |
Non-work activities |
1616
(44.37) |
2026
(55.63) |
1219.16
(244.70) |
Work
activities |
Workplace |
1242
(85.83) |
205
(14.17) |
178.19
(236.08) |
439.38
(150.49) |
| Home |
399
(64.77) |
217
(35.23) |
30.21
(100.89) |
178.62
(183.60) |
| Other places |
102
(43.78) |
131
(56.22) |
12.44
(66.59) |
194.40
(184.58) |
| 2020 |
Non-work activities |
1853
(46.39) |
2141
(53.61) |
1228.52
(242.39) |
Work
activities |
Workplace |
957
(80.22) |
236
(19.78) |
127.62
(215.77) |
427.25
(166.83) |
| Home |
844
(79.85) |
213
(20.15) |
74.95
(163.40) |
283.21
(204.75) |
| Other places |
75
(44.64) |
93
(55.36) |
8.91
(59.53) |
211.89
(203.63) |
| Covid-19 variable |
| Variable |
Number of individuals (%) |
| 2019 |
2020 |
| No COVID-19 |
3642 (100.00) |
122 (3.05) |
| Mild incidence COVID-19 |
0 (0.00) |
3485 (87.26) |
| High incidence COVID-19 |
0 (0.00) |
387 (9.69) |
Table A2.Sample description of exogenous variables.
| Variable |
Number of individuals (%) |
Chi-square
test p-valuea |
| 2019 |
2020 |
| Age |
| Age 18-24 |
242 (6.64) |
258 (6.46) |
0.75 |
| Age 25-29 |
312 (8.57) |
330 (8.26) |
| Age 30-39 |
849 (23.31) |
961 (24.06) |
| Age 40-49 |
829 (22.76) |
859 (21.51) |
| Age 50-64 |
1080 (29.65) |
1221 (30.57) |
| Age > 64 |
330 (9.06) |
365 (9.14) |
| Genders |
| Female |
1796 (49.31) |
1947 (48.75) |
0.62 |
| Male |
1846 (50.69) |
2047 (51.25) |
| Education |
| Below bachelor’s degree |
1947 (53.46) |
2069 (51.80) |
0.12 |
| Bachelor’s degree |
965 (26.50) |
1143 (28.62) |
| Postgraduate degree |
730 (20.04) |
782 (19.58) |
| Annual household income |
| Low income (< USD 35,000) |
547 (15.02) |
473 (11.84) |
0.00 |
| Medium income (USD 35,000-74,999) |
1283 (35.23) |
1405 (35.18) |
| High income (>= USD 75,000) |
1812 (49.75) |
2116 (52.98) |
| Employment status |
| Unemployment |
139 (3.82) |
262 (6.56) |
0.00 |
| Managers, professionals, education- and art-related employees |
1173 (32.21) |
1293 (32.37) |
| Service/manual labor, healthcare, and legal-related employees |
1958 (53.76) |
2026 (50.73) |
| Self-employed workers |
372 (10.21) |
413 (10.34) |
| Metropolitan status |
| Non-metropolitans |
543 (14.91) |
537 (13.45) |
0.07 |
| Metropolitans |
3099 (85.09) |
3457 (86.55) |
| Interactions of income and metropolitan status |
| Low-income x Metropolitan status |
| Low income metropolitans |
439 (12.05) |
374 (9.36) |
0.00 |
| Non-low income metropolitans |
3203 (87.95) |
3620 (90.64) |
| Medium-income x Metropolitan status |
| Medium income metropolitans |
1043 (28.64) |
1161 (29.07) |
0.68 |
| Non-medium income metropolitans |
2599 (71.36) |
2833 (70.93) |
| High-income x Metropolitan status |
| High income metropolitans |
1617 (44.40) |
1922 (48.12) |
0.00 |
| Non-high income metropolitans |
2025 (55.60) |
2072 (51.88) |
a Contingency table chi-square test: H0 – the distribution of categories in 2020 is not different from that of 2019
Appendix B. Detailed occupations for the two occupational employee categories.
- Managers, professionals, education and art-related employees
(1) Management occupations
(2) Business and financial operations occupations
(3) Computer and mathematical science occupations
(4) Architecture and engineering occupations
(5) Education, training, and library occupations
(6) Arts, design, entertainment, sports, and media occupations
(7) Life, physical and social science occupations
- Service/manual labor, healthcare, and legal-related employees
(1) Sales and related occupations
(2) Office and administrative support occupations
(3) Food preparation and serving related occupations
(4) Building and grounds cleaning and maintenance occupations
(5) Farming, fishing, and forestry occupations
(6) Construction and extraction occupations
(7) Installation, maintenance, and repair occupations
(8) Production occupations
(9) Transportation and material moving occupations
(10) Personal care and service occupations
(11) Healthcare practitioner and technical occupations
(12) Healthcare support occupations
(13) Community and social service occupations
(14) Legal occupations
(15) Protective service occupations
Appendix C. Methodology to calculate the average treatment effects and probability-weighted average treatment effects for the latent-class multiple discrete-continuous extreme value model.
Average treatment effects (ATE) are used to compare differences between a pair of outcomes (from a model or experiment), where one is assumed to undergo treatment and the other does not receive any treatment. In our study, mild and high incidence of COVID-19 were considered as the treatments affecting people’s time allocated to work. In this context, this appendix first describes the method of calculating traditional ATE based on situations that all observations have an equal weight (arithmetic average) and then outlines why and how one may calculate probability-weighted average treatment effects (WATE) when using estimates from latent-class discrete-continuous extreme value (MDCEV) models.
To investigate the ATE based on the estimates from the latent-class MDCEV model, we first used 200 random draws to generate fitted values (Yk,nc,s) of time allocated to each one of the k alternatives (k =1, 2, 3, 4; non-work activities, work at workplace, work at home, and work at other places, respectively) in (s) scenarios: (1) without COVID-19 (control), (2) and with mild (treatment 1), and (3) high (treatment 2) COVID-19 incidences. Then, to characterise differences in effects based on class membership, we assigned individuals to the class that they had the highest probability of belonging (c = 1 if Class 1 or c = 2 if Class 2). For example, if an individual (n) had a 0.32 and 0.68 probability of belonging to Class 1 and Class 2, respectively, they were assigned to Class 2 (n2). Treatment effects were then computed within each class as the relative differences between the fitted values in the treatment and control situations.
Treatment 1: ATE for all individuals=1NcNc∑nc=1(Yk,nc,2−Yk,nc,1)Treatment 2: ATE for all individuals=1NcNc∑nc=1(Yk,nc,3−Yk,nc,1)
where Nc is the total number of individuals in each class. Effects were also stratified based on socio-demographic groups (g):
Treatment 1: ATE for each socio-demographic group=1NgcNgc∑nc=1(Yk,nc,2−Yk,nc,1)Treatment 2: ATE for each socio-demographic group=1NgcNgc∑nc=1(Yk,nc,3−Yk,nc,1)
where Ngc represents the total number of individuals in each socio-demographic group in each class.
The computation of ATE using an arithmetic average (as shown in equations 1 and 2) does not accommodate for the fact that in latent class models, the probability of belonging to a class varies across individuals. For example, in the computation above, an individual with a 0.51 and 0.49 probability of belonging to Class 1 and Class 2, respectively, and an individual with a 0.99 and 0.01 probability of belonging to Class 1 and Class 2, respectively, will both be assigned to Class 1 and contribute equally to the ATE if they have the same fitted values. However, the latter should have a more substantial contribution to the aggregate effect. Therefore, to account for this variation in the probability of belonging to a class, a probability-weighted average treatment effect (WATE) can be calculated.
To compute the weights for each individual (Wnc), we first calculated the differences between their probability of belonging to class c (either Class 1 or 2) and the average probability of belonging to this class for all class members. Then, we added one to this difference to avoid negative values. Wnc=1+(Pnc−1nc∑Ncnc=1Pnc) was then applied to weigh the fitted values:
WYk,nc,s=Yk,nc,s∗(1+(Pnc−1ncNc∑nc=1Pnc) )
where WYk,nc,s is the probability-weighted fitted values. Moreover, before computing the WATE, to ensure that each individual’s total available time would remain 1,440 minutes per day after adding weights, WYk,nc,swas adjusted by the ratio of 1,440 min to the total weighted fitted values of time allocated across all alternatives:
WY′k,nc,s=WYk,nc,s∗1440∑Kk=1WYk,nc,s
Weighted treatment effects were then computed within each class by calculating the difference of the effects in treatment and control situations.
Treatment 1: WATE for all individuals=1NcNc∑nc=1(WY′k,nc,2−WY′k,nc,1)Treatment 2: WATE for all individuals=1NcNc∑nc=1(WY′k,nc,3−WY′k,nc,1)
Additionally, probability-weighted effects were also stratified based on socio-demographic groups:
Treatment 1: WATE for each socio-demographic group=1NgcNgc∑nc=1(WY′k,nc,2−WY′k,nc,1)Treatment 2: WATE for each socio-demographic group=1NgcNgc∑nc=1(WY′k,nc,3−WY′k,nc,1)